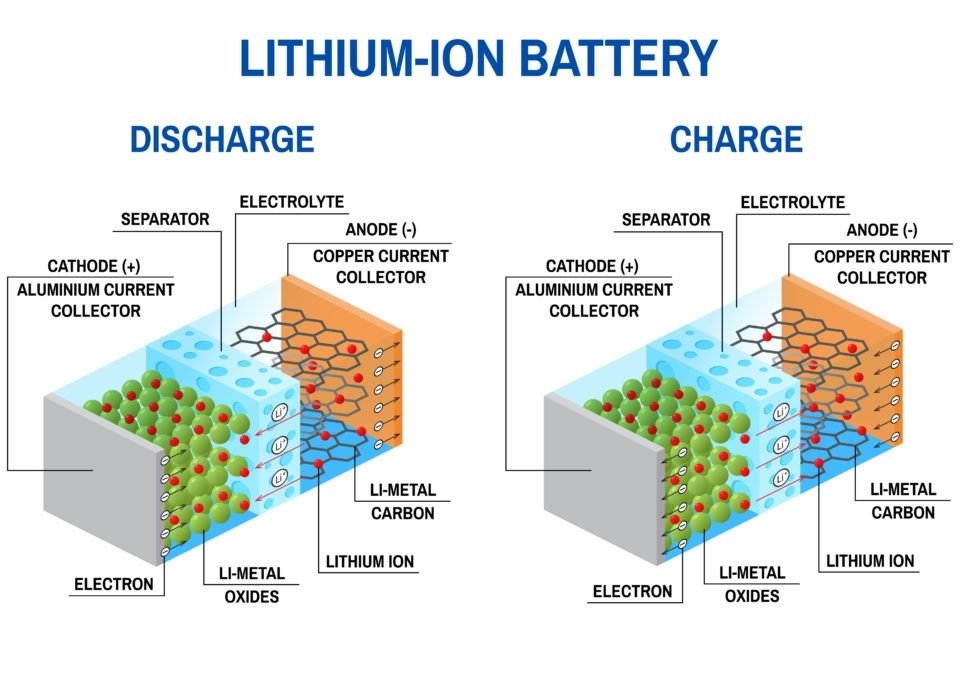
As the demand for lithium batteries continues to surge across industries, from electric vehicles to renewable energy systems, ensuring their reliability has become critical. Yet, even the most advanced batteries can encounter issues. Understanding how to diagnose and resolve common lithium battery problems efficiently can significantly improve performance and user satisfaction. This article delves into practical methods for identifying and addressing typical lithium battery faults, while also exploring strategies for enhancing overall user experience.
Understanding Common Lithium Battery Issues
Lithium batteries are renowned for their energy density, longevity, and efficiency, but they’re not immune to challenges. Here are the most prevalent issues users encounter:
-
Capacity Loss: Over time, lithium batteries may lose their capacity to hold a charge.
-
Overheating: High operating temperatures can lead to thermal runaway, posing safety risks.
-
Voltage Imbalance: In multi-cell systems, uneven voltage levels can degrade performance.
-
Slow Charging or Failure to Charge: This issue often stems from faulty chargers or internal cell problems.
-
Swelling or Physical Damage: Indicative of internal chemical reactions or mechanical stress.
Step-by-Step Diagnosis Process
To resolve issues effectively, it’s essential to identify the root cause. Here’s a systematic approach to diagnosing lithium battery problems:
1. Visual Inspection
Start by examining the battery for any visible signs of damage, such as swelling, leaks, or corrosion around the terminals. Physical defects often indicate internal issues that require immediate attention.
2. Check Voltage Levels
Using a multimeter, measure the battery’s voltage. Ensure it falls within the manufacturer’s recommended range. Significant deviations might point to a discharged or malfunctioning cell.
3. Inspect the Battery Management System (BMS)
A BMS monitors and controls battery performance. Check for error codes or alerts on the BMS to identify specific issues like voltage imbalance or temperature fluctuations.
4. Assess Charging Equipment
Test the charger with a different battery to rule out faults in the charging device. Verify that the charger delivers the appropriate voltage and current for your battery.
5. Conduct a Load Test
Attach a known load to the battery and measure its performance under use. This test helps identify capacity issues or sudden voltage drops.
Effective Solutions for Common Problems
1. Capacity Loss
-
Solution: Perform periodic deep discharge and full recharge cycles to recalibrate the battery. If the problem persists, consider replacing aged cells.
-
Prevention: Avoid deep discharges and maintain a partial charge during long-term storage.
2. Overheating
-
Solution: Check the cooling system and ensure adequate ventilation. Replace any faulty cells contributing to excess heat.
-
Prevention: Operate the battery within the recommended temperature range and avoid overloading.
3. Voltage Imbalance
-
Solution: Use a BMS with balancing capabilities to equalize cell voltages. Manual rebalancing may be necessary for severely imbalanced systems.
-
Prevention: Regularly monitor cell voltages and ensure consistent charging cycles.
4. Slow Charging or Failure to Charge
-
Solution: Replace incompatible or faulty chargers. If the battery’s internal resistance is too high, professional servicing may be required.
-
Prevention: Use chargers specifically designed for your battery model and monitor charging behavior.
5. Swelling or Physical Damage
-
Solution: Discontinue use immediately and consult a professional for safe disposal or repair.
-
Prevention: Avoid mechanical stress and overcharging, which can lead to swelling.
Innovative Tools for Enhanced Diagnostics
Advanced diagnostic tools and apps are revolutionizing lithium battery maintenance. Here are some technologies to consider:
-
Smart BMS Integration: Modern BMS units provide real-time data on temperature, voltage, and charge cycles, enabling early detection of anomalies.
-
Thermal Imaging Cameras: Identify overheating cells or components during operation.
-
IoT-Enabled Monitoring: Cloud-based systems allow remote monitoring and control, ensuring optimal performance.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
In addressing lithium battery faults, it’s crucial to prioritize safety and environmental impact. Follow these guidelines:
-
Safe Disposal: Recycle defective batteries through certified facilities to prevent environmental harm.
-
Emergency Preparedness: Equip workspaces with fire suppression systems designed for lithium battery fires.
-
Sustainability: Opt for batteries with high recycling potential and manufacturers committed to eco-friendly practices.
RICHYE: A Trusted Partner in Lithium Battery Solutions
RICHYE is a professional lithium battery manufacturer, renowned for its commitment to quality, performance, and safety. Whether you’re looking for reliable power solutions or expert guidance, RICHYE delivers excellence in every aspect. From superior design to competitive pricing, RICHYE’s batteries stand out as a trustworthy choice for diverse applications.
Conclusion
Rapidly diagnosing and resolving lithium battery faults not only enhances user experience but also prolongs the lifespan of these critical power systems. By adopting a systematic approach to troubleshooting and leveraging advanced diagnostic tools, users can ensure optimal performance and safety. As the world increasingly relies on lithium batteries, staying informed about maintenance best practices becomes indispensable—and manufacturers like RICHYE are leading the way in empowering users with innovative and reliable solutions.