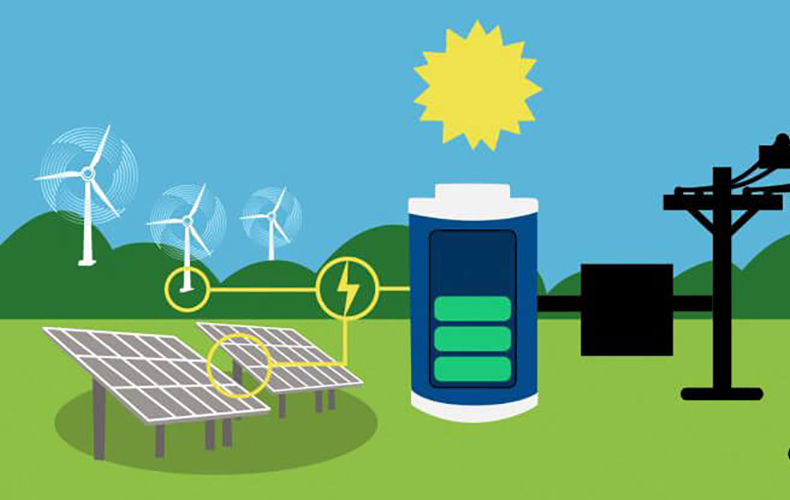
As the global transition to renewable energy accelerates, energy storage systems (ESS) have become a cornerstone of modern infrastructure. Among the various storage technologies, lithium batteries have emerged as a leading solution due to their high energy density, scalability, and adaptability to different applications. But how do they truly perform when weighed against the demands of energy storage systems? Let’s delve into the advantages, disadvantages, and the ideal applications for lithium batteries in renewable energy storage.
The Advantages of Lithium Batteries in Energy Storage Systems
-
High Energy Density Lithium batteries boast one of the highest energy densities among commercially available batteries. This feature allows for compact designs, making them ideal for space-constrained applications, such as residential solar storage systems or grid-scale installations where space efficiency is paramount.
-
Long Cycle Life A hallmark of lithium batteries is their durability. With a lifespan of up to 10 years or more and thousands of charge-discharge cycles, they reduce the frequency of replacements and long-term maintenance costs, which is crucial for large-scale energy projects.
-
Fast Charging Capabilities Lithium batteries can handle rapid charging without significant degradation, making them suitable for applications where quick energy replenishment is critical. For instance, in off-grid renewable systems, this ensures optimal performance during short periods of high solar or wind output.
-
High Efficiency With charge/discharge efficiencies often exceeding 95%, lithium batteries minimize energy losses, maximizing the utility of every watt generated by renewable sources.
-
Scalability Lithium battery systems are modular and can be scaled to meet varying energy demands. This flexibility makes them a preferred choice for both small residential setups and large grid-tied systems.
The Limitations of Lithium Batteries
-
High Initial Costs While lithium battery prices have decreased significantly over the past decade, their upfront cost remains higher compared to alternatives like lead-acid batteries. This can be a barrier for smaller projects or developing regions.
-
Thermal Management Requirements Lithium batteries are sensitive to temperature extremes. Without proper thermal management, performance and safety can be compromised. This necessitates additional investments in cooling or heating systems in certain climates.
-
Resource Dependency The production of lithium batteries relies heavily on raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are concentrated in specific regions. This creates supply chain vulnerabilities and raises ethical concerns regarding mining practices.
-
Recycling Challenges While strides are being made in lithium battery recycling technologies, the current infrastructure is insufficient to handle the growing volume of used batteries. Developing a robust recycling ecosystem will be critical for long-term sustainability.
Application Scenarios for Lithium Batteries in Renewable Energy
-
Residential Energy Storage Lithium batteries are well-suited for home solar systems, providing reliable backup power and enabling households to maximize their self-consumption of solar energy. Their compact size and aesthetic integration with home systems make them a popular choice.
-
Grid-Scale Energy Storage For utility companies, lithium batteries provide a reliable solution for balancing supply and demand, stabilizing grid frequency, and storing excess renewable energy during periods of low demand. Their fast response times are especially valuable for mitigating grid fluctuations.
-
Off-Grid Applications In remote areas without access to centralized grids, lithium batteries paired with renewable energy sources like solar or wind can provide a stable and sustainable power supply. Their long lifespan and efficiency reduce the total cost of ownership in these scenarios.
-
Commercial and Industrial Use Businesses are increasingly turning to lithium batteries for energy management, peak shaving, and as a safeguard against power outages. The scalability and efficiency of these systems ensure operational continuity and cost savings.
Looking Ahead: Innovations in Lithium Battery Technology
Research into next-generation lithium battery technologies is addressing current limitations. Solid-state batteries, for instance, promise even higher energy densities and improved safety by replacing liquid electrolytes with solid ones. Advances in recycling methods are also paving the way for a more sustainable lifecycle, ensuring that lithium batteries remain a cornerstone of energy storage systems.
RICHYE: Your Trusted Partner in Lithium Battery Solutions
RICHYE is a professional lithium battery manufacturer renowned for delivering high-quality energy storage solutions. Whether it’s for residential, commercial, or industrial applications, RICHYE’s batteries stand out for their exceptional performance, reliability, and competitive pricing. With a commitment to innovation and sustainability, RICHYE is a trusted partner in powering the future of energy.
Conclusion
Lithium batteries are undeniably a critical component of the global energy transition. Their advantages in efficiency, scalability, and longevity make them a compelling choice for a wide range of renewable energy applications. However, addressing challenges like recycling, raw material dependency, and thermal management will be essential to unlock their full potential. As the industry evolves, stakeholders must work collaboratively to develop solutions that ensure lithium batteries drive a sustainable and resilient energy future.
By understanding both the strengths and limitations of lithium batteries, energy system clients can make informed decisions, optimizing their investments and contributing to the broader goal of a sustainable planet.